Albert Einstein was a German mathematician and physicist who developed the special and general theories of relativity. He won the Nobel Prize for physics for his explanation of the photoelectric effect in 1921.

E=m.c2; energy of a body (E) is equal to the mass (m) of that body times the speed of lights squared (c2). This equation suggested that tiny particles of mattes could be converted into huge amounts of energy a discovery that heralded atomic power. Famed quantum theorist Max Planck backed up the assertions of Einstein who thus became a star of the lecture circut and academia taking on various positions before becoming director of the Kasier Wilhelm Institute for physics from 1913 to 1933.
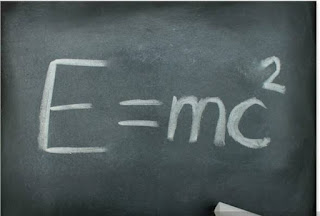
I think a lot about how his daily life was.
YanıtlaSil